Scrutinizing your fetus during labor and the tail end of your pregnancy is shared practice. A fetal heart monitor made by Fetal Monitor manufacturers is used to check the rate, beat, and speed up or slowing down of the fetal heartbeat. The normal heartbeat for a fetus is between 110 and 160 beats per minute and may swap due to the circumstances in the uterus. If the fetal monitor notices there is an irregular heart rate, that could mean the fetus is not getting sufficient oxygen or can be revealing other glitches. Sometimes the OB-GYN or your healthcare professional will say that cesarean distribution is required. It is significant to remember that an irregular heart rate does not always mean that the fetus is at risk.
When Electronic Fetal Monitoring (EFM) is used, two main apparatuses are checked. The first is the heart degree and the second is the reduction of the uterus. If you have been in labor then you might recall a nurse attaching two girdles, each with a ring sensor on them. Both of these devices are connected to a fetal monitoring machine such as the Philips Avalon FM50. The Avalon FM50 is a cutting-edge fetal heart monitor that also has the choice to non-invasively monitor motherly vital signs as well as the vitals of the fetus.
The sensors refer to and notice data that is understood by the fetal recording machine and show the baby’s heart rate and mother’s shrinkages on printed paper or shown on the machine. The heart rate and shrinkages presented together are often named EFM tracings. Once the starting point is set for the heart rate of the fetus, the machine will then evaluate the variations of the heart rate with the mother’s contractions.
How is Fetal Monitoring Done?
- First, a cream is applied to the mother’s stomach that acts as a medium between the skin and the ultrasound transducer.
- Second, the ultrasound transducer is committed to the stomach with a girdle to help keep it in place.
- Third, to screen contractions a second sensor is positioned on the stomach to monitor maternal reductions. This device is named a tocodynamometer.
Irregular Fetal Heart Rate?
If your fetal heart rate is irregular this does not always mean that there is a drawback. Your OB-GYN or healthcare expert will achieve other examinations to get an idea of what is going on. Stages can be taken to aid the baby get more oxygen like altering your position. If these actions do not work, your OB-GYN may agree to deliver right away.
Internal Fetal Heart Monitor?
The technique of nursing your baby’s heart rate above is named external fetal monitoring. You might have also gotten internal fetal monitoring, but what is internal fetal monitoring?
An internal fetal heart monitor supplied by Fetal Monitor suppliers uses an electronic transducer that is more minor than the one used for external monitoring. This transducer is coupled right to the baby’s skin. This transducer electrode is characteristically devoted to the scalp or another body part that is available through the cervical opening. The electrode is occasionally named a scalp electrode. Internal fetal monitoring delivers a more accurate and reliable analysis. Your OB-GYN or healthcare professional may put in an internal fetal monitor electrode if scrutinizing the fetal heart rate externally is insufficient, or closer investigation is required.
How do Fetal Monitors Effort?
A fetal heart monitor senses FHR (Fetal Heart Rate) by using an ultrasound transducer to convey and obtain ultrasonic waves. The Frequency change of the reproduced signal is compared to the speed of the shimmering structure. A transducer comprises one or more piezoelectric fundamentals that adopt an electrical signal into ultrasonic energy that can be conveyed into tissues. When the ultrasonic energy is reproduced back from the tissues, the transducer reconverts it back to an electrical signal that is understood by the fetal monitor device and displayed on the screen or a printout.
Why do I Need a Fetal Monitor?
A fetal heart monitor is used closely every pregnancy to evaluate fetal well-being and recognize any changes that might be related to glitches during pregnancy or labor. Monitoring the fetal heart rate is particularly vital for high-risk pregnancy circumstances such as glitches with fetal growth, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Some circumstances that might disturb the heart rate are uterine reductions, medicates, and pushing during labor.
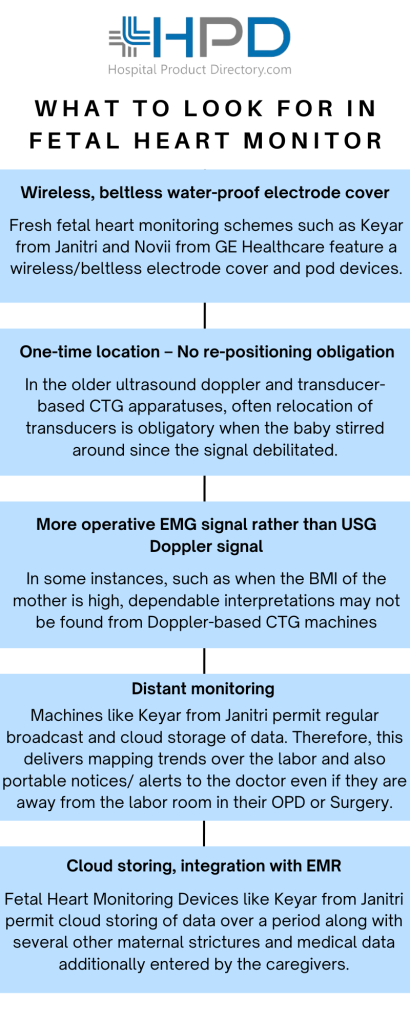
What aspects to look for in Fetal Heart Monitors?
- Wireless, Beltless Water-proof Electrode Cover for Better Flexibility & Liberty
Fresh fetal heart monitoring schemes such as Keyar from Janitri and Novii from GE Healthcare feature a wireless/beltless electrode cover and pod devices. Unlike the Doppler-based topography NST apparatuses, where the mother has to be in bed linked to all the wires monitoring the heart rates and shrinkages, a wireless electrode patch machine bought from Fetal Monitor Dealers permits the mother to transfer around in the room and change her location even if lying down easily.
- One-time Location – No Re-positioning Obligation
In the older ultrasound doppler and transducer-based CTG apparatuses, often relocation of transducers is obligatory when the baby stirred around since the signal debilitated. No such re-positioning of electrodes is obligatory in the newer wireless machines. Fetal Heart monitoring machines like Keyar and Novii use EMG signals to track FHR, MHR, and UC, which is robust enough no matter, how much fetal movement is there.
- More Operative EMG Signal Rather than Ultrasound Doppler Signal
In some instances, such as when the BMI of the mother is high, dependable interpretations may not be found from Doppler-based CTG machines, while the EMG signal-based newer wireless machines acquire dependable tracings on even high BMI patients by scrutinizing electrical signals on the patient’s stomach, which are not conceded by high BMI.
- Distant Monitoring
Machines like Keyar from Janitri permit regular broadcast and cloud storage of data. Therefore, this delivers mapping trends over the labor and also portable notices/ alerts to the doctor even if they are away from the labor room in their OPD or Surgery.
- Cloud Storing, integration with EMR, and in-built Examined Data
Fetal Heart Monitoring Devices like Keyar from Janitri permit cloud storing of data over a period along with several other maternal strictures and medical data additionally entered by the caregivers. This could be combined with the Electronics Medical Records of the patient for better analytics and medical outcome. If appropriate data is documented, it mechanically helps compute ROBSON Arrangement, BISHOP score, or APGAR score, etc.
Recent developments in Fetal Heart Monitoring systems certainly look promising from the point of view of augmented patient comfort & safety and greater help to doctors and caregivers.